As Summer starts to wind down, I thought this would be a good poem. In fact, it’s one of the few about Summer in the Hyakunin Isshu:
| Japanese | Romanization | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| 風そよぐ | Kaze soyogu | In the evening |
| ならの小川の | Nara no ogawa no | when the wind rustles the oaks |
| 夕ぐれは | Yugure wa | at Nara-no-Ogawa, |
| みそぎぞ夏の | Misogi zo natsu no | it is the ablutions that are |
| しるしなりける | Shirushi narikeru | the only sign it’s still summer! |
The author of this poem is Ju-ni-i Ietaka (従二位家隆, 1158 – 1237), or “Ietaka of Junior Second Rank”. His personal name was Fujiwara no Ietaka, and that he was the son-in-law of Jakuren (poem 87), and studied poetry under Fujiwara no Shunzei (poem 83). In fact he was so talented that he became the tutor for a young Emperor Gotoba (poem 99). After the Emperor’s exile following the Jokyu War, Ietaka and Gotoba still corresponded and shared poems.
My new book suggests that this might be why Teika (poem 97), compiler of the Hyakunin Isshu, put them next to one another (poems 98 and 99) numerically.
The notion of ablution or misogi (禊ぎ) is a Shinto ritual involving purification through cold water, prayer, etc. The practice is still alive and well today, and is often done in the summer months, but it varies depending on the particular Shinto shrine. In Shinto, people accumulate impurities through bad actions or traumatic events, and have to expunge them through ritual to balance their lives. As Professor Mostow explains, it was also popular in the author’s time as a well of making up for carrying on illicit affairs too. 😉
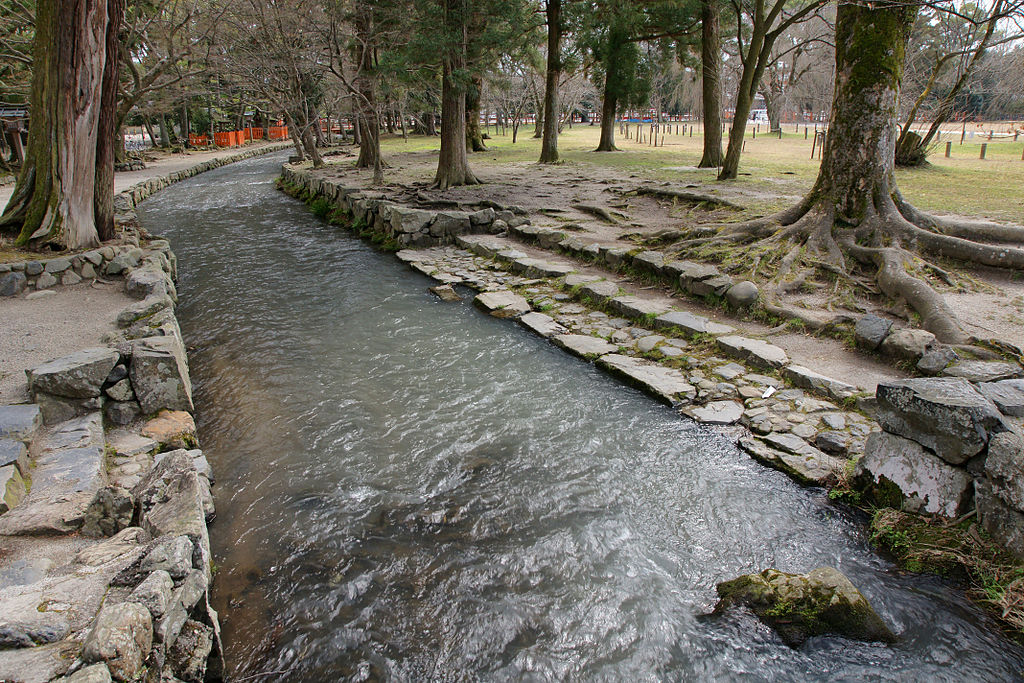
According to the Hyakunin Isshu Daijiten, the second verse of the poem is a good example of a kakekotoba ( 掛詞) wordplay, in that it has two meanings. First, nara can mean an oak tree (楢), especially Quercus serrata trees. The second meaning, nara no ogawa, refers to the font at the upper Kamo Shrine also called the Kamigamo Shrine (kamigamo-jinja, 上賀茂神社). The homepage can be found here.

Another concept in late summer is the notion of zansho (残暑) which is the long, hot, humid summer that comes after the monsoon season in June-July. Speaking from first-hand experience, it’s stifling hot, but here the poem implies that the summer is nearly over, and only the ablutions remain.
P.S. Featured photo is of Iyagatani (伊屋ヶ谷) waterfall, of Ryujuin (龍樹院) Temple. Photo by 松岡明芳, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons